Sequence Properties are found in the Properties window.
Sequence identifier & name property
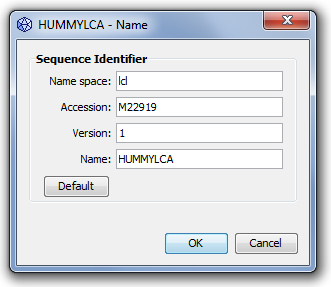
A simple name such as "albumin" is not sufficient to identify uniquely a biological sequence. For example, different versions of the same sequence may coexist or the same sequence may be accessed in different databases. Genbeans uses a sequence identifier to name a sequence; although this identifier is mostly used internally, it can be accessed through the property "name". This is the place to edit the identifier.
-
Name space: Define a context for a set of sequences, such as for example "embl" for EMBL database sequences or a user name for user's sequences stored on a local computer. By default and in most cases with this version of GenBeans, the name space is "lcl", meaning local.
-
Accession: Accession number for database access. The accession number is composed of alphanumeric characters.
-
Version: An integer, by default 0. A version number can be defined only when an accession is defined.
-
Name: A name.
The Default button is not currently used.
Sequence type
Four types of sequences are recognized: DNA, RNA, Protein, and Unknown.
Length
The length of the sequence.
GC content
Percentage of G and C content, for nucleotide sequences only.
Tm
Melting temperature in standard PCR conditions, for oligonucleotides of less than 100 bases.
Circularity
Circularity of nucleotide sequences.
MW
Molecular weight of polypeptides.
pI
Isoelectric point of polypeptides.