The EMBL Nucleotide Sequence Database constitutes Europe's primary nucleotide sequence resource. The EMBL-Bank is part of the International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration, which comprises the DNA DataBank of Japan (DDBJ), the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), and GenBank at NCBI.
EMBL Format
EMBL format is text-based. Following is an example of an EMBL record; note that only the beginning of the record is shown:

It is a multisequence format and each sequence is terminated by a double-slash sign ('//'). For detailed information on EMBL format, please consult the EMBL site.
EMBL files and extensions
By default, files terminated by the extension "embl" are recognized by the Explorer and displayed with an EMBL icon (![]() ). Associations between EMBL files and extensions can be adjusted in the Options > Miscellaneous > Files panel.
). Associations between EMBL files and extensions can be adjusted in the Options > Miscellaneous > Files panel.
Viewing EMBL files in the Explorer
To view the sequences contained in an EMBL file, click on the plus ('+') sign in front of the node as follow:
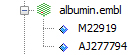
if GenBeans fails to parse a sequence, an error sign will be shown in the explorer:
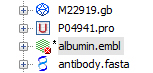
The other records of the file will be valid as long as the double-slash separators ('//') are properly located.
Contextual menu
You can access the contextual menu by right-clicking the mouse on the sequence node or the file node:
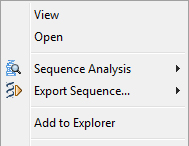
• Open: Open the EMBL file in the Editor at the first line of the sequence.
• Sequence Analysis: Access to varied sequence analyses such as translation, restriction analysis, etc.
• Export Sequence: Export to a new file in varied formats.
The EMBL editor
Opening files in the Editor
To open an EMBL file, either double-click on the corresponding node in the Explorer or choose the menu File > Open from the main menu to access the file dialog. Once opened in the editor, the EMBL file is automatically parsed and highlighted appropriately. The color schema can be adjusted in the Fonts & Colors category of the Options panel. When an error in the format is encountered, a special red highlight is shown in the editor as in the following example:
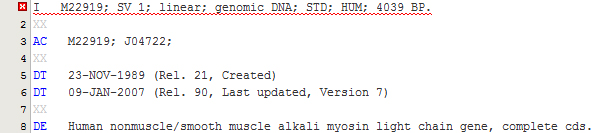
Editing EMBL records
By default, EMBL files cannot be edited manually. EMBL format is complex and requires a precise knowledge of each tag formatting and is at best generated by a software. Note that EMBL records can be easily corrupted when edited manually. If you need to edit a record anyway, first unlock editing by clicking the locking state button (![]() ) in the editor toolbar; edit your sequence manually. As you type, GenBeans parses the file and create an internal representation of each sequence record. At any time you can click on the refresh button (
) in the editor toolbar; edit your sequence manually. As you type, GenBeans parses the file and create an internal representation of each sequence record. At any time you can click on the refresh button (![]() ) located in the same toolbar; as a result, GenBeans synchronizes the record with its internal sequence representation and fixes all feature locations automatically. Note that when sequence data are modified, GenBeans compares the new data with the previous one and calculate the part of the sequence that has changed. All features overlapping this section will be removed during a refresh action. Finally relock the editing by clicking the locking state button (
) located in the same toolbar; as a result, GenBeans synchronizes the record with its internal sequence representation and fixes all feature locations automatically. Note that when sequence data are modified, GenBeans compares the new data with the previous one and calculate the part of the sequence that has changed. All features overlapping this section will be removed during a refresh action. Finally relock the editing by clicking the locking state button (![]() ) in the editor toolbar.
) in the editor toolbar.
Contextual menu
Right-click anywhere in a record to access a specific contextual menu.